
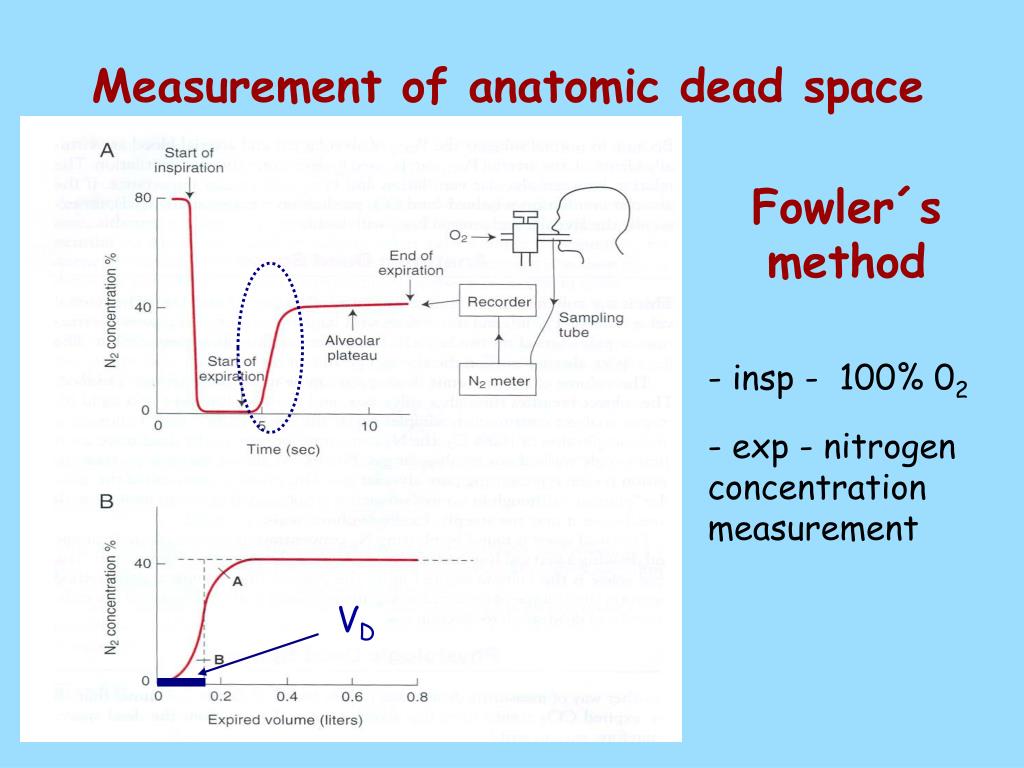
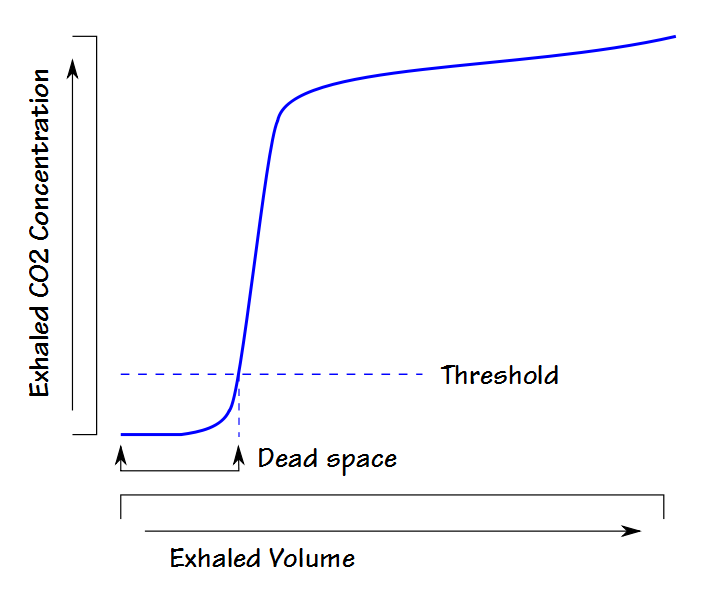
Physiologic dead space is the sum of airway dead Alveolar dead space is a measurement of ventilatedĪlveoli without adequate blood flow for gas exchange and is negligible Predict changes in lung volume following acute lung injury.Īirway dead space is a functional surrogate of anatomic dead spaceĪnd is calculated from Phase II of the C volume curve from aĬapnograph (10). Single breath C analysis has also been shown to Recent advances inĬapnography technology have provided a simplified method for calculating Used to identify pulmonary embolism (7,8). There are several established useful clinical applicationsįor /. (/), and is a clinical measure of the efficiency of Volume, also known as physiologic dead space ratio Dead space is often expressed as a ratio of dead space to tidal It includes both alveolar and airway dead Involved in gas exchange and can be considered ineffective inĪrterialising venous blood. Of early tracheostomy argue that decreases in anatomic dead space lowerĪirway resistance, allow lower peak inspiratory pressures and may evenĬhange dynamic compliance, resulting in reduction of the work ofīreathing, thus allowing patients to wean off the ventilatorĮxpeditiously and decrease ventilator days (5).ĭead space is defined as the portion of the respiratory system not Tracheostomy is thought to facilitate weaning by reducing dead space andĪirway resistance and by improving secretion clearance (5). These are attributable to fundamental changes in respiratory dynamics. However, there is a lack of consensus as to whether The ventilator, incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia and use of
Early tracheostomy may decrease the time on The benefits and advantages of tracheostomy have been vigorouslyĭebated for several decades. Of tracheostomy has evolved to be used mainly in patients withĭifficulty weaning from mechanical ventilation (2). Since the advent of positive pressure ventilation in the 1950s, the use Tracheostomy was described primarily for emergent airway obstruction. Literature for the relief of respiratory insufficiency during the polioĮpidemic in the 1930s (1). Wilson and Davidson first described tracheostomy in modern Growing population of patients who require prolonged ventilatory Advances in resuscitation, improvements in clinical care andĬhanges in the delivery of mechanical ventilation have resulted in a Tracheostomy is a surgical procedure routinely performed uponĬritically ill patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilatory Space, airway resistance, work of breathing Key Words: critical care, tracheostomy, respiratory dynamics, dead Respiratory mechanics and dead space with a tracheostomy versus This study shows that there is no significant difference in Significant change in dead space, compliance or other respiratory The average dead space of endotracheal versus Only two (8%) of the patients had slight improvement (>6%ĭecrease in dead space). Prior to tracheostomy and repeated within 24 hours of tracheostomy. Non-invasive cardiac output 2 device (Phillips, Andover, MA) immediately Respiratory parameters were measured using the Respironics' Ventilator settings and sedation were kept consistent throughout the Internal diameters between endotracheal tube and tracheostomy tubes, The diameter of the endotracheal tubes ranged fromĦ-8 mm and the tracheostomy tube diameters were from 6.4-8.9 mm. Necessary either for severe neurological devastation or failure to weanįrom the ventilator. With various aetiologies of respiratory failure. Twenty-four intubated patients were included in our analysis On dead space, airway resistance and other lung parameters in criticallyĭata collected included patients who were admitted to surgical,īurn and neurosurgical intensive care units at the University of NorthĬarolina. We compare the effect of tracheostomy versus endotracheal tube Improvement is attributable to fundamental changes in respiratoryĭynamics. There is a lack of consensus as to whether perceived clinical Retrieved from īenefits and advantages of tracheostomy have been vigorouslyĭebated.
#ANATOMIC DEAD SPACE FREE#
MLA style: "Tracheostomy in the critically ill: the myth of dead space." The Free Library.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
